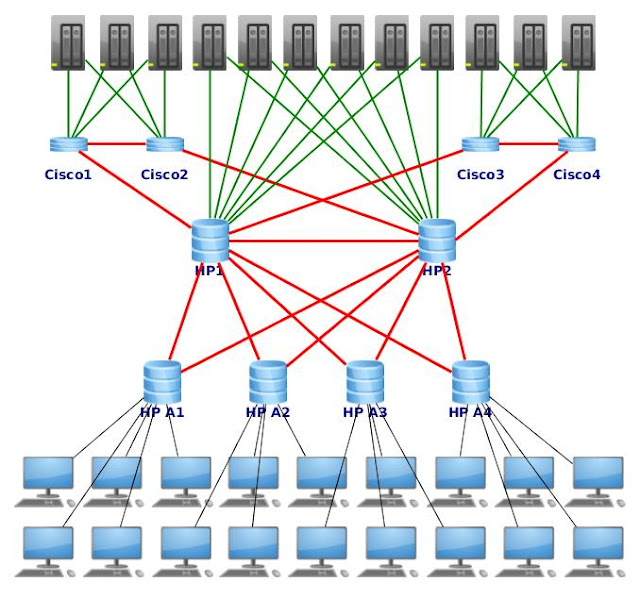
Building a fault tolerant network infrastructure for your company.
PortFast - This mode is intended to "speed up" the initialization of the ports that are connected to servers or user stations. In the normal state, without PortFast, a port with active Spanning Tree before switching to data forwarding mode goes through several pretty long phases: blocked, listening, learning, and only after 40-50 seconds, port switched to forwarding and begins to transmit data. This is done in order for have time for discover a loop or double link on initialization stage of Spanning Tree, and we do not had problems with our network even for a short time. If to the port connected a workstation or a server, we do not need such a long procedure, it may be even harmful for the workstation or server! For example, a computer may not have a time for get an address from DHCP, if loading of computer faster than is initialized port.
So, when we activate PortFast, a port skip phases of listening and learning, and immediately becomes to forwarding state. When you turn on PortFast, Spanning Tree continues to work on these ports, it will not turn off! Continues to send and receive BPDU. Moreover, if the port with activated PortFast, has received message BPDU, it immediately loses its status, despite settings. Nevertheless, is not recommended to enable PortFast on ports connected to another network equipment, because it may lead to appearing routing loops for short time.
Cisco:
On Cisco have two ways to activate this mode: locally on specific ports or globally in configuration mode.
Global:
spanning-tree portfast default
This command enables PortFast on all ports which in access mode.
How to enable:
spanning-tree A1-A2 admin-edge-port
sh run:
spanning-tree A1 admin-edge-port
spanning-tree A2 admin-edge-port
sh run:
no spanning-tree A1 auto-edge-port
no spanning-tree A2 auto-edge-port
Sorry for my English...
Part 3: Additional tuning for boundary and user ports on Cisco and HP ProCurve.
Today we look at what can do to protect our STP topology on the access ports, and at borders to other networks. Let's start with the most basic settings, such as PortFast, BPDUGuard, BPDUFilter and specific option for ProCurve - PVST-Filter.
PortFast
PortFast - This mode is intended to "speed up" the initialization of the ports that are connected to servers or user stations. In the normal state, without PortFast, a port with active Spanning Tree before switching to data forwarding mode goes through several pretty long phases: blocked, listening, learning, and only after 40-50 seconds, port switched to forwarding and begins to transmit data. This is done in order for have time for discover a loop or double link on initialization stage of Spanning Tree, and we do not had problems with our network even for a short time. If to the port connected a workstation or a server, we do not need such a long procedure, it may be even harmful for the workstation or server! For example, a computer may not have a time for get an address from DHCP, if loading of computer faster than is initialized port.
So, when we activate PortFast, a port skip phases of listening and learning, and immediately becomes to forwarding state. When you turn on PortFast, Spanning Tree continues to work on these ports, it will not turn off! Continues to send and receive BPDU. Moreover, if the port with activated PortFast, has received message BPDU, it immediately loses its status, despite settings. Nevertheless, is not recommended to enable PortFast on ports connected to another network equipment, because it may lead to appearing routing loops for short time.
Cisco:
On Cisco have two ways to activate this mode: locally on specific ports or globally in configuration mode.
Global:
spanning-tree portfast default
This command enables PortFast on all ports which in access mode.
Local:
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
spanning-tree portfast
Or despite an active global settings, you can disable PortFast on the ports where it is not needed:
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
spanning-tree portfast disable
Also, in some cases you may to enable PortFast on trunk's, for example, it may be necessary if the trunk connected to a server that needs to get several VLAN's from trunk.
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
spanning-tree portfast trunk
Checking PortFast state on interface:
sh spanning-tree int gi0/1 portfast
MST0 enabled
MST2 enabled
Also:
sh spanning-tree int gi0/1 detail
Port 1 (GigabitEthernet0/1) of MST0 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 20000, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.1.
Designated root has priority 4096, address 001b.3fc1.a800
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 001d.e691.2800
Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 3
The port is in the portfast mode by default
Link type is point-to-point by default, Internal
Bpdu guard is enabled by default
Loop guard is enabled by default on the port
BPDU: sent 174100, received 0
Port 1 (GigabitEthernet0/1) of MST2 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 20000, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.1.
Designated root has priority 2, address 0018.71b6.a000
Designated bridge has priority 32770, address 001d.e691.2800
Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 22000
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 2
The port is in the portfast mode by default
Link type is point-to-point by default, Internal
Bpdu guard is enabled by default
Loop guard is enabled by default on the port
BPDU: sent 174100, received 0
Here you can see if the port has lost its PortFast status. To return PortFast mode, you need to disable and enable this interface:
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
shutdown
no shutdown
HP ProCurve:
On ProCurve have analog of PortFast called "edge-port", for manual setup port mode to "EDGE" you may use option "admin-edge-port". By default for all ports active "auto-edge-port" mode, which determine port mode (edge(PortFast) or no). And I should be noted that this automatic feature on ProCurve works very well! Port very quickly turns into EDGE mode when needed, and quickly lose it status, if received BPDU message.How to enable:
spanning-tree A1-A2 admin-edge-port
sh run:
spanning-tree A1 admin-edge-port
spanning-tree A2 admin-edge-port
Forced disable automatic detection of edge ports:
no spanning-tree A1-A2 auto-edge-port
sh run:
no spanning-tree A1 auto-edge-port
no spanning-tree A2 auto-edge-port
Return to auto-edge-port mode and disable admin-edge-port:
spanning-tree A1-A2 auto-edge-port
and
no spanning-tree A1-A2 admin-edge-port
Checking edge port status:
sh spanning-tree A1
Port Type | Cost rity State | Bridge Time PtP Edge
------ ---------- + --------- ---- ------------ + ------------- ---- --- ----
A1 100/1000T | 20000 128 Forwarding | 001b3f-582100 2 Yes No
and also
sh spanning-tree A1 detail
AdminEdgePort : No
Auto Edge Port : Yes
Switch is in mst mode (IEEE Standard)
Root bridge for: none
Extended system ID is enabled
Portfast Default is enabled
PortFast BPDU Guard Default is enabled
Portfast BPDU Filter Default is disabled
Loopguard Default is enabled
EtherChannel misconfig guard is enabled
UplinkFast is disabled
BackboneFast is disabled
On Cisco BPDUGuard may be switched locally on the interface or globally. Regardless of the method of activation, when receiving an incoming BPDU on the port with the activated BPDUGuard, a port will blocked.
Cisco:
Local:
interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
spanning-tree bpduguard enable / disable
As in the case Portfast, "disable" disables the global settings for a particular port.
Global (automatically activate BPDUGuard on all PortFast interfaces):
spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
In the next article I will add information about loop-guard, loop-protect and udld. I will additionally compose in one article all about fight against loops on managed and unmanaged hardware. It will be last article about Spanning Tree and LAN topology. Then we turn to fault-tolerant of internet access and cluster technologies :)
sh spanning-tree A1
Port Type | Cost rity State | Bridge Time PtP Edge
------ ---------- + --------- ---- ------------ + ------------- ---- --- ----
A1 100/1000T | 20000 128 Forwarding | 001b3f-582100 2 Yes No
sh spanning-tree A1 detail
AdminEdgePort : No
Auto Edge Port : Yes
OperEdgePort : No
BPDUFilter
This feature disables the reception and transmission of BPDU on the port. It can be used for different purposes, such as protection against foreign Spanning Tree on the link to the provider or to other neighbors, with whom you have only single link. To protect against attacks based on BPDU and as a consequence, instability of your topology.
Cisco:
On Cisco BPDUFilter as PortFast may be enabled through two ways: globally in configuration mode, and locally on the interface. But unlike PortFast, BPDUFilter have different behavior, depending on the method of activation.
Local:
interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
spanning-tree bpdufilter enable / disable
As in the case PortFast, "disable" disables the global settings for a particular port.
Global (automatically activate BPDUFilter on all PortFast interfaces):
Global (automatically activate BPDUFilter on all PortFast interfaces):
spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default
When you turn on BPDUFilter locally on the interface, this works as "the wall", it equivalent to disabling Spanning Tree on the interface. BPDU do not go to any direction. In some cases, it may be dangerous. For example, in case connecting port with activated BPDUFilter to neighboring port, you get a loop that will not eliminate by Spanning Tree, and if you not have other anti-loop means, your network will be collapse. So, be careful using this function locally at the interface.
If this feature is enabled globally, it is not dangerous, because it is activated on the PortFast ports, and blocks only sending BPDU, but not blocks receiving. Global BPDUFilter disabled on the port when receiving first BPDU packet from outside. This feature is more suitable to mask your BPDU from foreign neighbors, than for blocking it. And as soon as your interface received the first BPDU package, you start working with a neighbor on the Spanning Tree.
When you turn BPDUFilter globally, there is another interesting feature: through the port during initialization will be sent a several BPDU messages, to make sure that this port is not contains devices STP. When you turn on BPDUFilter on the local port, will be blocked any BPDU for sent and receive.
Checking BPDUFilter state:
sh spanning-tree summary Switch is in mst mode (IEEE Standard)
Root bridge for: none
Extended system ID is enabled
Portfast Default is enabled
PortFast BPDU Guard Default is enabled
Portfast BPDU Filter Default is disabled
Loopguard Default is enabled
EtherChannel misconfig guard is enabled
UplinkFast is disabled
BackboneFast is disabled
Checking BPDUFilter state on interface:
sh spanning-tree int gi0/1 detail
Port 1 (GigabitEthernet0/1) of MST0 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 20000, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.1.
Designated root has priority 4096, address 001b.3fc1.a800
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 001d.e691.2800
Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 3
The port is in the portfast mode by default
Link type is point-to-point by default, Internal
Bpdu guard is enabled by default
Bpdu filter is enabled
Loop guard is enabled by default on the port
BPDU: sent 174100, received 0
Port 1 (GigabitEthernet0/1) of MST2 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 20000, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.1.
Designated root has priority 2, address 0018.71b6.a000
Designated bridge has priority 32770, address 001d.e691.2800
Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 22000
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 2
The port is in the portfast mode by default
Link type is point-to-point by default, Internal
Bpdu guard is enabled by default
Bpdu filter is enabled
Bpdu filter is enabled
Loop guard is enabled by default on the port
BPDU: sent 174100, received 0
HP ProCurve:
On ProCurve BPDUFilter need to enable on each port:
spanning-tree A1-A2 bpdu-filter
sh run:
spanning-tree A1 loop-guard bpdu-filter
spanning-tree A2 loop-guard bpdu-filter
Show ports with activated BPDUFilter:
sh spanning-tree | i Filter
BPDU Filtered Ports : A1-A2
spanning-tree A1-A2 bpdu-filter
sh run:
spanning-tree A1 loop-guard bpdu-filter
spanning-tree A2 loop-guard bpdu-filter
Show ports with activated BPDUFilter:
sh spanning-tree | i Filter
BPDU Filtered Ports : A1-A2
also:
sh spanning-tree A1 detail
BPDU Filtering : Yes
Also, HP has another nice feature, which is useful in the case of using MSTP, and may help in described in this article case: Part 2: " Connect Cisco and HP ProCurve using MSTP". In the article described the case when Cisco in MST mode, going crazy with receiving PVST message, flown through ProCurve topology.
PVST-Filter! Enabling like BPDUFilter:
spanning-tree A1-A2 pvst-filter
sh run:
spanning-tree A1 pvst-filter
spanning-tree A2 pvst-filter
Show PVST-Filter status:
sh spanning-tree | i PVST
PVST Filtered Ports : A1-A2
also:
sh spanning-tree a1 det
PVST Filtering : Yes
Maybe, if you are using MSTP, this function must be activated on all ports, because nothing good from receiving PVST not will be. At least MSTP and PVST are inconsistent, and may be many problems like in my previons article: Part 2: " Connect Cisco and HP ProCurve using MSTP"...
BPDUGuard
Cisco:
Local:
interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
spanning-tree bpduguard enable / disable
As in the case Portfast, "disable" disables the global settings for a particular port.
Global (automatically activate BPDUGuard on all PortFast interfaces):
spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
If the port is blocked, you need to disable and enable this interface:
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
shutdown
no shutdown
Either setup automatic enable blocked ports using errdisable recovery:
errdisable recovery cause bpduguard
errdisable recovery interval 60
Checking BPDUGuard state:
sh spanning-tree summary
PortFast BPDU Guard Default is enabled
Checking BPDUGuard state on interface:
sh spanning-tree int gi0/1 detail
Port 1 (GigabitEthernet0/1) of MST0 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 20000, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.1.
Designated root has priority 4096, address 001b.3fc1.a800
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 001d.e691.2800
Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 3
The port is in the portfast mode by default
Link type is point-to-point by default, Internal
Bpdu guard is enabled by default
Loop guard is enabled by default on the port
BPDU: sent 174100, received 0
Port 1 (GigabitEthernet0/1) of MST2 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 20000, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.1.
Designated root has priority 2, address 0018.71b6.a000
Designated bridge has priority 32770, address 001d.e691.2800
Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 22000
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 2
The port is in the portfast mode by default
Link type is point-to-point by default, Internal
Bpdu guard is enabled by default
Loop guard is enabled by default on the port
BPDU: sent 174100, received 0
HP Procurve:
On ProCurve BPDUGuard called BPDU-Protection:
spanning-tree A1-A2 bpdu-protection
sh run:
spanning-tree A1 loop-guard bpdu-protection
spanning-tree A2 loop-guard bpdu-protection
Show ports with activated BPDU-Protection:
sh spanning-tree | i Protect
BPDU Protected Ports : A1-A16,A18-A24,B1-B24,C1-C24,D1-D24,G...
sh spanning-tree a1 detail | i Protect
BPDU Protection : Yes
In my opinion BPDUGuard very useful, as it allows to protect against unauthorized connection of network equipment, as well BPDUGuard is instantly blocks the majority of the loops. But BPDUGuard can also cause problems, for example if you activate BPDUGuard on interface that connected to the provider. From providers, by my experience, often arrives STP, which immediately lead to port blocking. I am very cautious, but on the interface to the service providers with whom we have only single connect, i am typically activate BPDUFIlter :)
In the next article I will add information about loop-guard, loop-protect and udld. I will additionally compose in one article all about fight against loops on managed and unmanaged hardware. It will be last article about Spanning Tree and LAN topology. Then we turn to fault-tolerant of internet access and cluster technologies :)
Sorry for my English...