Building a fault tolerant network infrastructure for your company.
Part 2: Connect Cisco and HP ProCurve using MSTP.
Part 1: "MSTP on HP ProCurve"
Part 3: "Additional tuning for boundary and user ports on Cisco and HP ProCurve"
на Русском
Continuing the series for "novice professionals" :) On the last time we made single network based on HP ProCurve, and today will be connecting Cisco equipment to our network, as on this scheme:
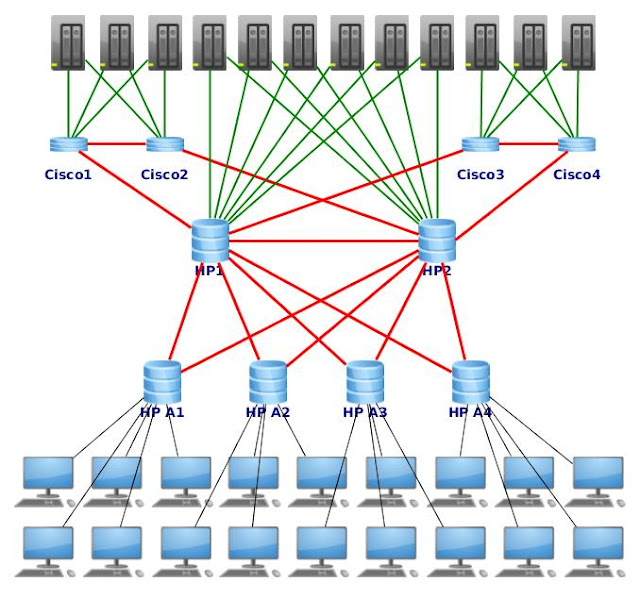 Connecting our Cisco 1, 2, 3 and 4, as shown in the scheme, but one of the links in each group of the two switches is turned off to prevent a loop, until Spanning Tree in not activated.
Connecting our Cisco 1, 2, 3 and 4, as shown in the scheme, but one of the links in each group of the two switches is turned off to prevent a loop, until Spanning Tree in not activated.
On ProCurve, we raised MSTP, it would be very good to raise MSTP on Cisco. In the Internet has a certain amount of information on the topic of linking ProCurve and Cisco, and even the official documentation from HP and from Cisco. But unfortunately...
Setup MSTP on Cisco.
For starters, if you have not read Part 1: "MSTP on HP ProCurve", I advise you to read! There i told the basic principles of setting MSTP on the switches, which are common to HP and for Cisco. Here is a brief list of recommendations Cisco and common sense to configure MSTP:
conf t
spanning-tree mst configuration
Do all as on the ProCurve. Region name the same as on ProCurve, the same as in all our the region:
name H2SO4
Config revision number must be the same in all network:
revision 1
Divide all VLAN on two "instances" according to the load on them in my network. In our case, as on ProCurve:
instance 1 vlan 1-35,101,111-500,1001-4094
instance 2 vlan 36-100,102-110,501-1000
Do not exit the configuration MST check the resulting configuration:
show pending
Pending MST configuration
Name [H2SO4]
Revision 1 Instances configured 3
Instance Vlans mapped
-------- ---------------------------------------------------------------------
0 none
1 1-35,101,111-500,1001-4094
2 36-100,102-110,501-1000
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Type "exit or press CTRL-Z for exit and applying the configuration:
exit
conf t
spanning-tree mst 1 root primary
spanning-tree mst 0-1 priority 0
spanning-tree mst 2 priority 4096
Cisco 2/4:
conf t
spanning-tree mst 2 root primary
spanning-tree mst 0-1 priority 4096
spanning-tree mst 2 priority 0
spanning-tree mode mst
Highlighted in blue is control sum, it must coincide with all configurations on HP and Cisco. If it is different - look for differences. So long as the digest is different, MSTP will work through the instance 0, and all the ports will be Boundary.
Cisco:
Name [H2SO4]
In this case, MSTP blocked not profitable route between switches for all instances, leaving him for the event of an accident.
Some statistics from Cisco:
sh spanning-tree mst 1
##### MST1 vlans mapped: 1-35,101,111-500,1001-4094
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi0/18 Desg FWD 20000 128.18 P2p
Gi0/20 Desg FWD 200000 128.20 P2p
Gi0/21 Desg FWD 200000 128.21 P2p
Gi0/22 Desg FWD 200000 128.22 P2p
Gi0/23 Desg FWD 200000 128.23 P2p
Gi0/24 Altn BLK 20000 128.24 P2p
Po1 Root FWD 20000 128.36 P2p
sh spanning-tree mst 2
##### MST2 vlans mapped: 36-100,102-110,501-1000
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi0/24 Altn BLK 20000 128.24 P2p
Po1 Root FWD 20000 128.36 P2p
Part 3: "Additional tuning for boundary and user ports on Cisco and HP ProCurve"
на Русском
Continuing the series for "novice professionals" :) On the last time we made single network based on HP ProCurve, and today will be connecting Cisco equipment to our network, as on this scheme:
 Connecting our Cisco 1, 2, 3 and 4, as shown in the scheme, but one of the links in each group of the two switches is turned off to prevent a loop, until Spanning Tree in not activated.
Connecting our Cisco 1, 2, 3 and 4, as shown in the scheme, but one of the links in each group of the two switches is turned off to prevent a loop, until Spanning Tree in not activated.Setup MSTP on Cisco.
For starters, if you have not read Part 1: "MSTP on HP ProCurve", I advise you to read! There i told the basic principles of setting MSTP on the switches, which are common to HP and for Cisco. Here is a brief list of recommendations Cisco and common sense to configure MSTP:
- Use the same "region" in all your network.
- Minimum number of instances.
- Set up the priorities for the "root bridge".
- In advance to divide the entire possible range of a VLAN on "instances".
- All instances on all switches in the region must contain the same list of VLANs! On Cisco will help protocol VTP v3, which is can to serve not only VLAN's, but also instances of MSTP. HP ProCurve has only GVRP, which is similar to VTP V1/2, but not work with MSTP, synchronization of instances settings between switches, perform by hands.
- Region name and config revision number must be the same throughout the network!
- Permission is granted an identical list of VLAN's on all tanks between commutators!
Also there are rules for connecting ProCurve and Cisco:
Check trunk between Cisco and ProCurve for permit of all necessary VLANs, and then proceed:- Cisco supports 802.1s MSTP only since 2005, make sure IOS later than 2005 year. In general FirmWare update on all equipment is good idea :)
- Not to be confused Pre-STD MST with MSTP - they are not compatible.
- Verify, that native/untagged VLAN 1 was set up on trunks between Cisco and HP.
conf t
spanning-tree mst configuration
Do all as on the ProCurve. Region name the same as on ProCurve, the same as in all our the region:
name H2SO4
Config revision number must be the same in all network:
revision 1
Divide all VLAN on two "instances" according to the load on them in my network. In our case, as on ProCurve:
instance 1 vlan 1-35,101,111-500,1001-4094
instance 2 vlan 36-100,102-110,501-1000
Do not exit the configuration MST check the resulting configuration:
show pending
Pending MST configuration
Name [H2SO4]
Revision 1 Instances configured 3
Instance Vlans mapped
-------- ---------------------------------------------------------------------
0 none
1 1-35,101,111-500,1001-4094
2 36-100,102-110,501-1000
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Type "exit or press CTRL-Z for exit and applying the configuration:
exit
If Cisco is root in the MSTP region, or your network is Cisco-Only, specify that our switches are root for specific instances in the MSTP region, as we did it on an HP in the last article, and set priorities for instances:Cisco 1/3:
conf t
spanning-tree mst 1 root primary
spanning-tree mst 0-1 priority 0
spanning-tree mst 2 priority 4096
Cisco 2/4:
conf t
spanning-tree mst 2 root primary
spanning-tree mst 0-1 priority 4096
spanning-tree mst 2 priority 0
For our configuration with Cisco and HP do not need to set up this priorities for Cisco, as the root bridge we use ProCurve, and all higher priorities are on the ProCurve!When we finished configuration of MSTP on all Cisco of group, you need to activate MSTP:
spanning-tree mode mst
All should work, if you followed the instructions, and your network is not hiding a unexpected surprise, as it happened in my network :)
I spent a few days trying to understand why MSTP between Cisco and HP do not work! As a result, in a dark corner was found the Cisco 3560, about which everyone has forgotten, and who worked in PVST mode... I never imagined that BPDU can fly through the entire network topology, and spoil life. In general, BPDU flys through network and Cisco drove crazy, when I enabled MSTP:
000068: 00:49:18: %SPANTREE-2-PVSTSIM_FAIL: Blocking root port Gi0/8: Inconsistent inferior PVST BPDU received on VLAN 110, claiming root 32878:0015.c6d7.9900
Gi0/7 Mstr BKN*20000 128.7 P2p Bound(PVST) *PVST_Inc
By the way, ProCurve have an option pvst-filter, perhaps this option can help without searching source of wrong BPDU.
So, what I did ... I turn on the Cisco debug for received BPDU:
term mon
debug spanning-tree bpdu receive
And I see this:
002836: Jan 5 16:36:57.625: STP: MST0 rx BPDU: config protocol = mstp, packet from GigabitEthernet0/8 , linktype IEEE_SPANNING , enctype 2, encsize 17
002837: Jan 5 16:36:57.625: STP: enc 01 80 C2 00 00 00 00 1B 3F 58 31 EF 00 89 42 42 03
002838: Jan 5 16:36:57.625: STP: Data 000003023C1000001B3FC1A800000000001000001B3FC1A80080110000140002000F00
002839: Jan 5 16:36:57.634: STP: MST0 Gi0/8:0000 03 02 3C 1000001B3FC1A800 00000000 1000001B3FC1A800 8011 0000 1400 0200 0F00
002840: Jan 5 16:36:58.238: STP: MST0 rx BPDU: config protocol = mstp, packet from GigabitEthernet0/8 , linktype SSTP , enctype 3, encsize 22
002841: Jan 5 16:36:58.238: STP: enc 01 00 0C CC CC CD 9C 4E 20 B2 2E 98 00 32 AA AA 03 00 00 0C 01 0B
002842: Jan 5 16:36:58.238: STP: Data 000000000080649C4E20B22E800000000080649C4E20B22E8080180000140002000F00
002843: Jan 5 16:36:58.238: STP: MST0 Gi0/8:0000 00 00 00 80649C4E20B22E80 00000000 80649C4E20B22E80 8018 0000 1400 0200 0F00
IEEE_SPANNING - it is normal.
А вот SSTP - It is abnormal. It is not our MSTP, it is a stranger Spanning-tree, source of this packet need to search!
Find the source of the package is very easy. The first 6 digits in the ENC is the header, it is always the same: 01 00 0C CC CC CD, but next 6 digits this is the sender's MAC address: 9C 4E 20 B2 2E 98 - in my case it was the Cisco 3560. After disabling STP all became normal. MSTP is working, and all became well.
Several commands for checking MSTP configuration on Cisco and HP:
HP:
I spent a few days trying to understand why MSTP between Cisco and HP do not work! As a result, in a dark corner was found the Cisco 3560, about which everyone has forgotten, and who worked in PVST mode... I never imagined that BPDU can fly through the entire network topology, and spoil life. In general, BPDU flys through network and Cisco drove crazy, when I enabled MSTP:
000068: 00:49:18: %SPANTREE-2-PVSTSIM_FAIL: Blocking root port Gi0/8: Inconsistent inferior PVST BPDU received on VLAN 110, claiming root 32878:0015.c6d7.9900
Gi0/7 Mstr BKN*20000 128.7 P2p Bound(PVST) *PVST_Inc
By the way, ProCurve have an option pvst-filter, perhaps this option can help without searching source of wrong BPDU.
So, what I did ... I turn on the Cisco debug for received BPDU:
term mon
debug spanning-tree bpdu receive
And I see this:
002836: Jan 5 16:36:57.625: STP: MST0 rx BPDU: config protocol = mstp, packet from GigabitEthernet0/8 , linktype IEEE_SPANNING , enctype 2, encsize 17
002837: Jan 5 16:36:57.625: STP: enc 01 80 C2 00 00 00 00 1B 3F 58 31 EF 00 89 42 42 03
002838: Jan 5 16:36:57.625: STP: Data 000003023C1000001B3FC1A800000000001000001B3FC1A80080110000140002000F00
002839: Jan 5 16:36:57.634: STP: MST0 Gi0/8:0000 03 02 3C 1000001B3FC1A800 00000000 1000001B3FC1A800 8011 0000 1400 0200 0F00
002840: Jan 5 16:36:58.238: STP: MST0 rx BPDU: config protocol = mstp, packet from GigabitEthernet0/8 , linktype SSTP , enctype 3, encsize 22
002841: Jan 5 16:36:58.238: STP: enc 01 00 0C CC CC CD 9C 4E 20 B2 2E 98 00 32 AA AA 03 00 00 0C 01 0B
002842: Jan 5 16:36:58.238: STP: Data 000000000080649C4E20B22E800000000080649C4E20B22E8080180000140002000F00
002843: Jan 5 16:36:58.238: STP: MST0 Gi0/8:0000 00 00 00 80649C4E20B22E80 00000000 80649C4E20B22E80 8018 0000 1400 0200 0F00
А вот SSTP - It is abnormal. It is not our MSTP, it is a stranger Spanning-tree, source of this packet need to search!
Find the source of the package is very easy. The first 6 digits in the ENC is the header, it is always the same: 01 00 0C CC CC CD, but next 6 digits this is the sender's MAC address: 9C 4E 20 B2 2E 98 - in my case it was the Cisco 3560. After disabling STP all became normal. MSTP is working, and all became well.
Several commands for checking MSTP configuration on Cisco and HP:
HP:
sh spanning-tree mst-config
MST Configuration Identifier Information
MST Configuration Identifier Information
MST Configuration Name : H2SO4
MST Configuration Revision : 1
MST Configuration Digest : 0xF1AD53AD5D69827DFCB5C5B5D00F6D88
IST Mapped VLANs :
Instance ID Mapped VLANs
----------- ---------------------------------------------------------
1 1-35,101,111-500,1001-4094
2 36-100,102-110,501-1000
Highlighted in blue is control sum, it must coincide with all configurations on HP and Cisco. If it is different - look for differences. So long as the digest is different, MSTP will work through the instance 0, and all the ports will be Boundary.
sh spanning-tree mst configuration
Name [H2SO4]
Revision 1 Instances configured 3
Instance Vlans mapped
-------- ---------------------------------------------------------------------
0 none
1 1-35,101,111-500,1001-4094
2 36-100,102-110,501-1000
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sh spanning-tree mst configuration digest
Name [H2SO4]
Revision 1 Instances configured 3
Digest 0xF1AD53AD5D69827DFCB5C5B5D00F6D88
Pre-std Digest 0x79EA425B9595B8B88B3E715854CC0CC8
In this case, MSTP blocked not profitable route between switches for all instances, leaving him for the event of an accident.
Some statistics from Cisco:
sh spanning-tree mst 1
##### MST1 vlans mapped: 1-35,101,111-500,1001-4094
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi0/18 Desg FWD 20000 128.18 P2p
Gi0/20 Desg FWD 200000 128.20 P2p
Gi0/21 Desg FWD 200000 128.21 P2p
Gi0/22 Desg FWD 200000 128.22 P2p
Gi0/23 Desg FWD 200000 128.23 P2p
Gi0/24 Altn BLK 20000 128.24 P2p
Po1 Root FWD 20000 128.36 P2p
sh spanning-tree mst 2
##### MST2 vlans mapped: 36-100,102-110,501-1000
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi0/24 Altn BLK 20000 128.24 P2p
Po1 Root FWD 20000 128.36 P2p
Documentation for configure HP and Cisco equipment together: from HP and from Cisco
The switches in a network we have collected, in following articles we will talk about setting ports for users, add protection from users and loops, make the fault-tolerant access to the internet and the fault-tolerant mail relay.
- Talk about BPDUGuard, BPDUFilter, PortFast, and about some features of the use of these services on the Cisco and HP ProCurve.
- We make a cluster of two servers based on FreeBSD + CARP for distribution Internet to users.
- We will make the cluster of two Debian / Ubuntu + UCARP for mail relay, relay mail between the Internet and the mail server or a cluster of company.
- We will make the cluster of two Cisco + HSRP for two channels from different internet providers.
Sorry for my English...


No comments:
Post a Comment